Vanilla
Vanilla planifolia
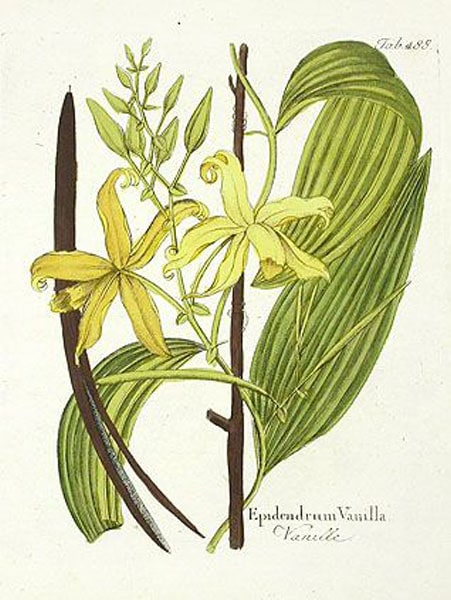
Family: Orchidaceae
Which probiotic is it in?:
Habit and cultivation: Native to Mexico, Central America and northern South America, it is the second most expensive spice after saffron. Grows in the warm, wet tropical low lands and forests. Can survive in nutritionally poor soil and can grow in total shade or semi-shade but is intolerant to wind. The flowers are pollinated by specific species of moth or by hand.
Actions (known for): Anti-microbial, anti-oxidant and anti-cancer.
History of Vanilla
Parts used from the Vanilla
Black seeds inside the beans.
Constituents (bio available chemicals):
Vanillin 85% of the bean. Vanillic acid, 4-Hydroxibenzaldehide, 4- Hydroxibenzoic acid, sugars, lipids, minerals and water.
Nutritional constituents:
Vitamins: B3. Minerals: calcium, magnesium, manganese, potassium, zinc and copper.
Indications:
Cancer and sickle cell anemia.
Dosage:
Varied
British Herbal Pharmacopoeia
Cautions for therapeutic doses
Adulteration and substitution issues due to the cost of pure vanilla.




































