Barberry
Berberis vulgaris
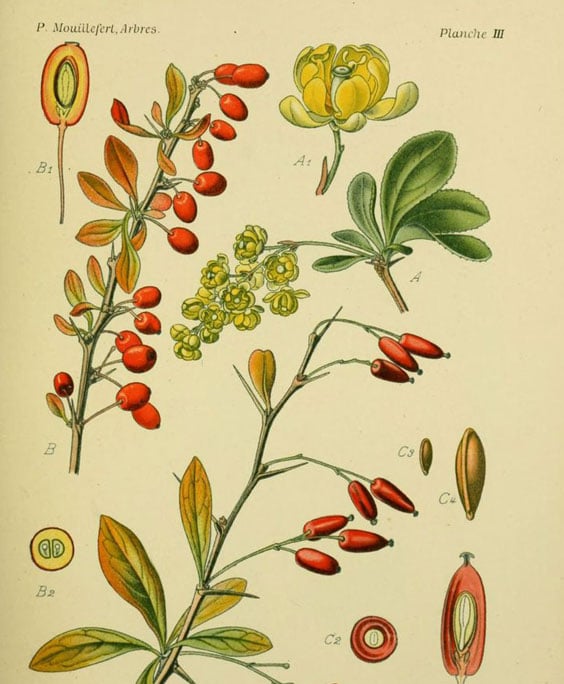
Family: Berberidaceae
Which probiotic is it in?: Barberry is a key herb in Detox
Habit and cultivation: The name Berberis is of unknown Latin origin. In Saxon the word means fence with thorns and the bush is used in fencing before the invention of fencing wire. European originally, introduced to England, Australia and New Zealand in the early 19 century. Grown from seed, cutting or layers, and can become a pest as self sowing. Frost resistant and drought tender.
Actions (known for): Alterative, aperient, cholagogue, digestive tonic, hepatotonic.
History of Barberry
Parts used from the Barberry
Root, root bark and stem bark.
Constituents (bio available chemicals):
Alkaloids: berberine, oxyacanthine, palmatine, berbamine. Chelidonic acid. Tannins. Wax. Resin.
Nutritional constituents:
Vitamin C. Minerals: Iron, copper, zinc and manganese.
Indications:
Acne, arthritis, boils, cholecystitis, gastrointestinal catarrh, eczema, gallstones, gallbladder disorders, gout, jaundice, psoriasis, skin disorders topically, urticaria.
Dosage:
Liquid extract (1:2): 20-40ml per week. Decoction: 0.5-1gm 3 x daily.
British Herbal Pharmacopoeia
Gallstones
Cautions for therapeutic doses
Pregnancy, first trimester.







