Moringa
oleifera
Family: Moringaceae
Which probiotic is it in?: Moringa is a key herb in Sustain, Women, Sleep, Immunity, Breathe, Kids and Detox.
Habit and cultivation: Native to tropical and subtropical regions of Southern Asia. India is still the largest producer. Moringa can grow in cooler regions but then only flowers annually whereas in more constant warm temperatures it can flower all year. This tree loves sun and heat. Manually harvested for the leaves, pods and kernels for oil extraction and water purification.
Actions (known for): Anti-oxidant, anti-convulsant, anti-cancer, anti-microbial, anti-trypanosomal, anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, anti-spasmodic and anti-glycaemic.
History of Moringa
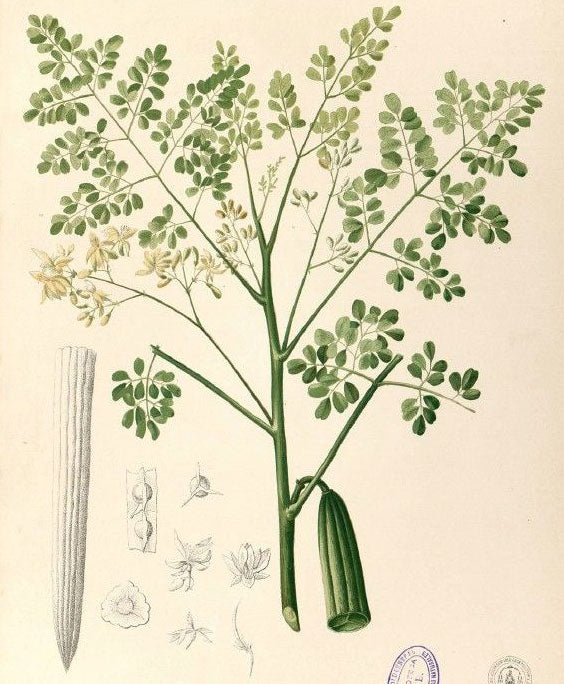
Parts used from the Moringa
Leaves, drumsticks (immature seed pods), seeds, seed oil and roots.
Constituents (bio available chemicals):
Flavonoids, glucosinolate, phenolic acid, terpenes, alkaloids and sterols.
Nutritional constituents:
Raw leaf and raw pods: protein, carbs, fats. Vitamins: A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C. Minerals: calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, sodium and zinc.
Indications:
Malnutrition from circumstance or disease. Considered a ‘super food’.
Dosage:
Varies considerably. Stick to what is written on the individual container.




































